Blockchain Use to Create an Online Business is revolutionizing the way operate, offering unparalleled security, transparency, and efficiency. By leveraging decentralized ledgers, smart contracts, and secure data management, blockchain enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance trust among stakeholders. From simplifying supply chain management to facilitating secure transactions and protecting intellectual property, the potential applications of blockchain in online business are vast and transformative. As the digital economy evolves, adopting blockchain can provide a competitive edge, ensuring robust and trustworthy operations in an increasingly interconnected world. Embrace the future of business with blockchain’s innovative solutions.
What Is Blockchain Business?
Key characteristics and applications of blockchain businesses include:
- Decentralization: Eliminating central authorities to foster peer-to-peer transactions.
- Transparency: Providing an immutable and publicly accessible record of transactions.
- Security: Ensuring data integrity and protection through cryptographic techniques.
- Smart Contracts: Automating and enforcing agreements without intermediaries.
- Supply Chain Management: Enhancing traceability and reducing fraud in supply chains.
- Digital Identity: Offering secure and verifiable identity solutions.
- Cryptocurrency Payments: Facilitating borderless and low-cost transactions.
How does blockchain work?
Here are some key advantages:
1. Data Structure
- Blocks: Information is stored in blocks, which contain a list of transactions. Each block has a unique code called a hash, generated using the data within the block and the hash of the previous block.
- Chain: Blocks are linked together in chronological order, forming a chain. This chain is immutable, meaning once a block is added, it cannot be altered without changing all subsequent blocks.
2. Decentralization
- Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network of nodes (computers). Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain and participates in the network’s validation and consensus processes.
3. Transaction Process
- Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, which is broadcast to the network.
- Validation: Nodes validate the transaction using a consensus mechanism, ensuring it follows the network’s rules.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Common methods include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add blocks.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
4. Block Addition
- Once validated, transactions are grouped into a block. The new block is added to the blockchain, linking it to the previous block via its hash.
5. Immutability and Security
- Each block’s hash is generated using the data within the block and the hash of the previous block. Changing any data in a block would alter its hash, breaking the chain and alerting the network to tampering.
- Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic techniques ensure data integrity and security.
6. Transparency and Trust
- The blockchain ledger is transparent and accessible to all network participants, fostering trust. Since the ledger is immutable, it provides a reliable and verifiable history of all transactions.
7. Smart Contracts
- Blockchain can also support programmable contracts, known as smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, automatically enforcing and executing agreements when predefined conditions are met.
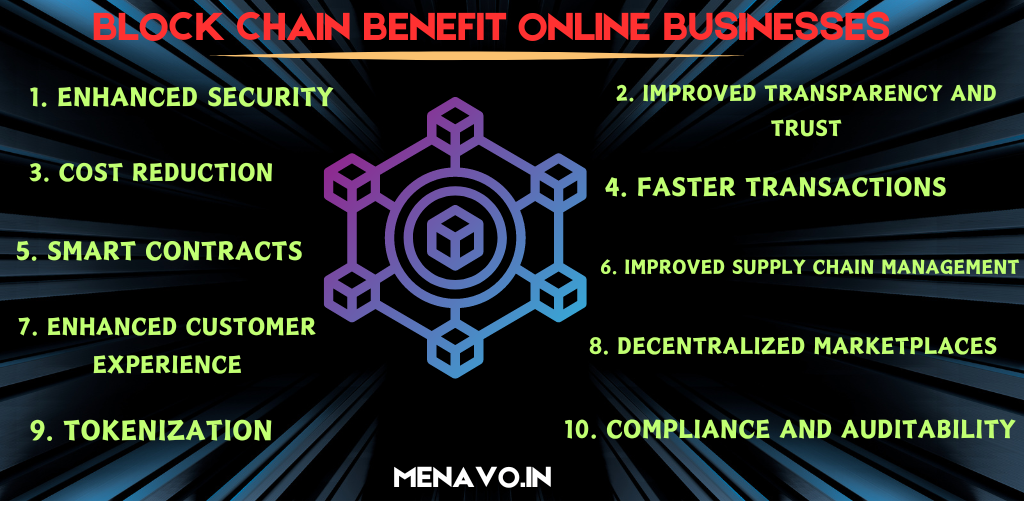
How can blockchain benefit Online businesses?
Here are some key advantages:
1. Enhanced Security
- Data Integrity: Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that transaction records cannot be altered or deleted, reducing the risk of fraud and data tampering.
- Cryptographic Protection: Transactions are encrypted, providing robust security against hacking and unauthorized access.
2. Improved Transparency and Trust
- Transparent Transactions: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, allowing customers and stakeholders to verify the authenticity of transactions.
- Traceability: Blockchain allows businesses to track the entire history of a product or transaction, enhancing transparency in supply chains and reducing counterfeiting.
3. Cost Reduction
- Eliminating Intermediaries: By enabling peer-to-peer transactions, blockchain reduces the need for middlemen, lowering transaction costs.
- Efficient Processes: Automating processes through smart contracts reduces administrative overhead and operational costs.
4. Faster Transactions
- Real-Time Settlements: Blockchain can process transactions 24/7, enabling faster settlements compared to traditional banking systems that operate on business hours.
5. Smart Contracts
- Automation: Smart contracts automatically execute and enforce agreements when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for manual intervention and legal enforcement.
- Reliability: These contracts are stored on the blockchain, ensuring they are tamper-proof and reliable.
6. Improved Supply Chain Management
- End-to-End Visibility: Blockchain provides real-time visibility into the supply chain, from production to delivery, enhancing efficiency and accountability.
- Reducing Fraud: By tracking products through every stage, businesses can ensure the authenticity of goods and reduce fraud.
7. Enhanced Customer Experience
- Loyalty Programs: Blockchain can streamline and secure loyalty programs, allowing for easy redemption and transfer of rewards.
- Data Privacy: Customers can have greater control over their personal data, enhancing trust and compliance with privacy regulations.
8. Decentralized Marketplaces
- Direct Transactions: Blockchain enables decentralized marketplaces where buyers and sellers can transact directly without intermediaries, reducing fees and enhancing security.
- Global Reach: Businesses can reach a global audience, leveraging blockchain’s borderless nature for international transactions.
9. Tokenization
- Asset Tokenization: Businesses can tokenize physical and digital assets, creating new opportunities for investment and ownership.
- Fundraising: Blockchain facilitates innovative fundraising methods such as Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Security Token Offerings (STOs).
10. Compliance and Auditability
- Regulatory Compliance: Blockchain’s transparent ledger makes it easier for businesses to comply with regulatory requirements and conduct audits.
- Automated Reporting: Smart contracts can automate compliance reporting, ensuring timely and accurate submissions.
Blockchain use cases in real-world industries?
Here are some key advantages:
1. Finance and Banking
- Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain enables faster and cheaper international transactions by eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction times from days to minutes.
- Fraud Prevention: The immutable ledger helps prevent fraudulent activities by ensuring the integrity and traceability of financial transactions.
- Smart Contracts: Automate loan agreements, insurance claims, and other financial contracts, reducing processing time and operational costs.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Product Traceability: Companies like Walmart and IBM use blockchain to track the origin and journey of products, enhancing transparency and accountability.
- Counterfeit Reduction: Ensures the authenticity of goods, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, by providing a verifiable history of each product.
3. Healthcare
- Patient Data Management: Securely stores and shares patient records, ensuring data privacy and improving the accuracy of medical histories.
- Drug Traceability: Blockchain helps track the production and distribution of pharmaceuticals, combating counterfeit drugs and ensuring regulatory compliance.
4. Real Estate
- Property Transactions: Streamlines the buying, selling, and leasing processes by recording property transactions on the blockchain, reducing the need for intermediaries and speeding up the process.
- Title Management: Ensures clear and transparent title ownership records, reducing disputes and fraud.
5. Voting Systems
- Secure Voting: Blockchain-based voting systems enhance the security and transparency of elections, ensuring that votes are tamper-proof and verifiable.
- Voter Identity Verification: Improves the integrity of voter registration and identity verification processes.
6. Energy Sector
- Energy Trading: Facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to buy and sell excess energy directly, promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
- Grid Management: Improves the efficiency of energy distribution and management through transparent and real-time tracking.
7. Retail and E-commerce
- Supply Chain Transparency: Retailers use blockchain to track the provenance of products, ensuring ethical sourcing and quality control.
- Loyalty Programs: Streamlines loyalty programs, allowing customers to easily earn and redeem rewards across different platforms.
8. Intellectual Property (IP)
- IP Protection: Blockchain provides a secure and immutable record of intellectual property rights, helping creators prove ownership and protect against infringement.
- Royalty Tracking: Ensures transparent and accurate tracking of royalty payments in industries like music, art, and publishing.
9. Government and Public Services
- Identity Management: Governments use blockchain to create secure digital identities for citizens, improving access to public services and reducing identity fraud.
- Land Registration: Blockchain enhances the transparency and security of land ownership records, reducing disputes and corruption.
10. Food and Agriculture
- Food Safety: Blockchain helps track the journey of food products from farm to table, ensuring safety and quality by identifying contamination sources quickly.
- Sustainable Farming: Enables transparent tracking of agricultural practices, promoting sustainable and ethical farming methods.
Blockchain jobs, roles and responsibilities?
Here are some key advantages:
1. Blockchain Developer
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Designing and Developing: Create and implement blockchain protocols, consensus algorithms, and decentralized applications (DApps).
- Smart Contract Development: Write and deploy smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum.
- Security: Ensure the security and integrity of blockchain applications and networks.
- Testing: Perform thorough testing and debugging of blockchain applications.
- Maintenance: Update and maintain existing blockchain solutions.
2. Blockchain Architect
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Design Architecture: Develop the architecture for blockchain solutions, including network nodes and infrastructure.
- Strategy and Planning: Define the overall technical strategy and implementation roadmap.
- Integration: Integrate blockchain solutions with existing systems and applications.
- Technology Evaluation: Assess and select appropriate blockchain platforms and technologies.
3. Blockchain Project Manager
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Project Planning: Define project scope, objectives, and deliverables.
- Team Coordination: Manage and coordinate between various teams involved in the project.
- Timeline Management: Ensure projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Stakeholder Communication: Act as the main point of contact between the development team and stakeholders.
- Risk Management: Identify and mitigate potential project risks.
4. Blockchain Consultant
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Advisory: Provide expert advice on blockchain adoption and implementation strategies.
- Solution Design: Design blockchain solutions tailored to client needs.
- Feasibility Analysis: Conduct feasibility studies and cost-benefit analyses.
- Training: Educate clients and their teams on blockchain technology and its applications.
5. Blockchain Analyst
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Market Research: Analyze trends, market conditions, and emerging technologies in the blockchain space.
- Data Analysis: Examine blockchain data to provide insights and inform decision-making.
- Reporting: Prepare detailed reports and presentations for stakeholders.
- Business Analysis: Identify potential blockchain applications and business opportunities.
6. Blockchain Quality Engineer
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Testing: Develop and execute test plans for blockchain applications.
- Automation: Implement automated testing solutions for blockchain environments.
- Performance Analysis: Monitor and analyze the performance of blockchain applications.
- Bug Tracking: Identify, report, and track defects and issues.
7. Cryptocurrency Developer
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Crypto Wallet Development: Design and develop secure cryptocurrency wallets.
- Blockchain Integration: Integrate cryptocurrencies with blockchain networks.
- Protocol Development: Develop and enhance cryptocurrency protocols and consensus mechanisms.
8. Blockchain Legal Consultant
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Regulatory Compliance: Advise on regulatory requirements and ensure compliance with relevant laws.
- Contract Drafting: Draft and review smart contracts and legal agreements.
- Risk Assessment: Identify and mitigate legal risks associated with blockchain implementations.
- Policy Development: Develop internal policies and guidelines for blockchain usage.
9. Blockchain Product Manager
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Product Vision: Define and communicate the product vision and strategy.
- Roadmap Development: Create and manage the product development roadmap.
- Feature Prioritization: Prioritize features and functionalities based on user needs and business goals.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Work with engineering, marketing, and sales teams to bring the product to market.
10. Blockchain Security Expert
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Security Audits: Conduct security audits of blockchain applications and networks.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identify and address potential security vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response: Develop and implement incident response plans.
- Best Practices: Establish security best practices and guidelines for blockchain development and deployment
What is the future of blockchain?
Here are some key advantages:
1. Mainstream Adoption
- Enterprise Integration: More businesses, from SMEs to large corporations, will integrate blockchain into their operations for enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency.
- Consumer Applications: Increased use of blockchain in everyday applications, such as digital identity verification, voting systems, and decentralized social networks.
2. Interoperability
- Cross-Chain Solutions: Development of technologies that enable different blockchains to communicate and interact seamlessly, enhancing the overall ecosystem.
- Standardization: Establishment of industry standards for blockchain protocols and platforms to ensure compatibility and interoperability.
3. Scalability Improvements
- Layer 2 Solutions: Adoption of Layer 2 scaling solutions like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and rollups for Ethereum, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions.
- New Consensus Mechanisms: Exploration of new consensus mechanisms that offer better scalability without compromising security and decentralization.
4. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Expansion
- Growth of DeFi Platforms: Continued growth and innovation in DeFi platforms, offering decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading services.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: Increased collaboration between DeFi and traditional financial institutions, potentially leading to hybrid financial products.
5. Regulatory Evolution
- Clearer Regulations: Development of clearer regulatory frameworks globally, providing guidance for businesses and investors while ensuring consumer protection.
- Compliance Solutions: Emergence of blockchain-based solutions that facilitate regulatory compliance and reporting.
6. Enhanced Security and Privacy
- Privacy Protocols: Implementation of advanced privacy protocols, such as zero-knowledge proofs, to enhance transaction privacy while maintaining transparency.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: Development of cryptographic methods resistant to potential threats from quantum computing.
7. Tokenization of Assets
- Real-World Asset Tokenization: Increased tokenization of real-world assets like real estate, commodities, and art, allowing for fractional ownership and improved liquidity.
- Digital Securities: Growth in the issuance and trading of digital securities (security tokens), providing new investment opportunities.
8. Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
- Widespread Adoption: Broader adoption of blockchain to enhance traceability, transparency, and efficiency in global supply chains.
- Sustainability Tracking: Use of blockchain to track and verify sustainable practices and ethical sourcing in supply chains.
9. Smart Cities and IoT Integration
- Smart Cities: Blockchain will play a crucial role in the development of smart cities, providing secure and transparent management of data and services.
- IoT Devices: Integration of blockchain with IoT devices to ensure secure data transmission, automated processes, and efficient resource management.
10. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- CBDC Development: Continued development and deployment of CBDCs by central banks worldwide, leveraging blockchain technology for secure and efficient digital currencies.
- Financial Inclusion: Potential for CBDCs to enhance financial inclusion by providing access to digital financial services for unbanked populations.